10 Powerful Gamification Examples in Education for 2025

In an era where engagement is the key to retention, educators are increasingly turning to game mechanics to transform learning. Gamification in education is not just about playing games; it's the strategic use of game-design elements like points, badges, and narrative quests to motivate students, foster collaboration, and make complex subjects more accessible. This shift addresses a critical need: to move beyond rote memorization and cultivate skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, and persistence.
By integrating these elements, learning becomes an active, rewarding experience rather than a passive one. Students are driven by clear goals, immediate feedback, and a sense of accomplishment, which boosts both their confidence and their ability to retain information. For a broader look at how gamification can transform education, explore these 10 Powerful Gamification in Learning Examples, which illustrate a range of successful applications. This approach creates more dynamic and effective learning environments across various platforms.
This article dives deep into specific gamification examples in education, breaking down the strategies that make them work. We will analyze everything from popular apps like Duolingo and Kahoot! to comprehensive systems like quest-based learning and virtual labs. For each example, we'll provide actionable takeaways you can apply to your own educational context. We will also consider how Polychat, a language learning app, leverages these principles to make mastering a new language an engaging and rewarding journey, free from frustrating limitations like hearts or energy systems. Get ready to explore the mechanics behind truly effective gamified learning.
Ready to Learn More?
Try PolyChat's interactive language learning games and put your new vocabulary to the test!
Games & Tools
Essential tools for every learner
Timed Challenges
Practice vocabulary & conjugation
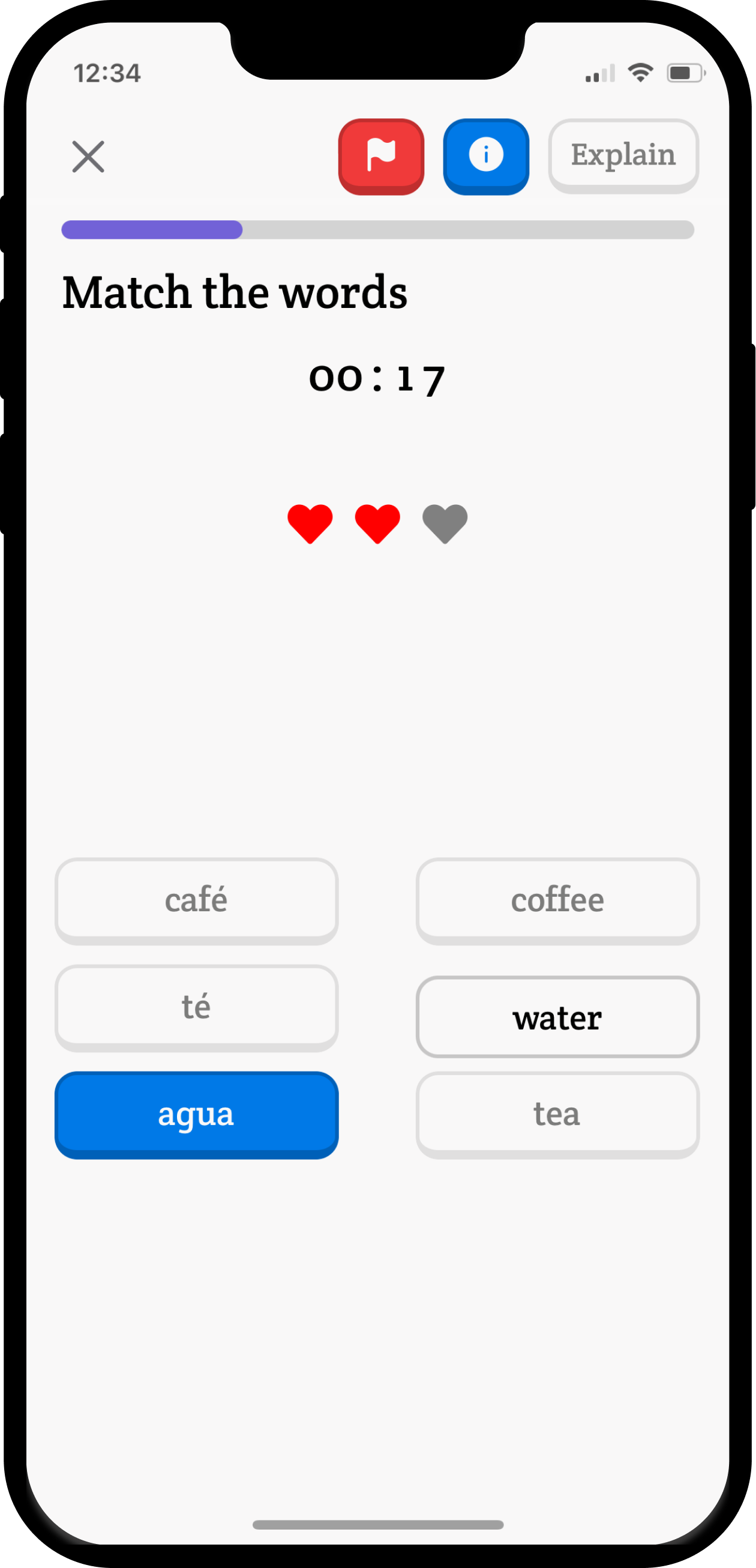
Interactive Games
Learn through engaging gameplay
1. Duolingo Language Learning App
Duolingo is a titan in educational technology, pioneering the use of gamification to make language learning accessible and engaging. It transforms the often tedious process of acquiring a new language into a game-like experience. Users complete bite-sized lessons to earn experience points (XP), maintain daily "streaks" for consistent practice, and compete on leaderboards, creating a powerful motivational loop.

The platform's success stems from its strategic blend of behavioral psychology and game design. By breaking down complex grammar and vocabulary into small, manageable challenges, Duolingo lowers the barrier to entry and builds user confidence. This approach is a prime example of how gamification in education can foster daily habits and long-term commitment.
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: Animated characters and celebratory sound effects provide immediate, positive feedback, tapping into the user's desire for accomplishment.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Leaderboards and achievement badges create a sense of competition and social validation, encouraging users to practice more to improve their standing.
- Habit Formation: The streak feature is a powerful tool for consistency. The fear of "breaking the chain" motivates users to log in daily, even if just for a few minutes, embedding language practice into their routine.
Key Insight: Duolingo's core strength lies in its ability to convert a long-term educational goal into a series of short-term, rewarding tasks. This makes the learning journey feel less daunting and more immediately gratifying.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Set Micro-Goals: Break down large assignments into smaller, daily tasks with clear completion rewards (e.g., points, badges).
- Visualize Progress: Implement a visual tracker, like a "streak" calendar or a progress bar, so students can see their consistent effort paying off.
- Encourage Friendly Competition: Use classroom leaderboards for specific activities, but ensure they are low-stakes to avoid discouraging struggling students.
- Incorporate Positive Reinforcement: Use immediate, encouraging feedback for correct answers or completed tasks to build momentum and confidence. You can discover more about Duolingo and similar tools in our detailed guide on gamification in language learning.
2. Points, Badges, and Leaderboards (PBL) Systems
Points, Badges, and Leaderboards (PBL) represent the foundational triad of gamification in education. This framework leverages simple, yet powerful, extrinsic motivators to drive engagement and track progress. Students earn points for completing tasks, receive badges for reaching specific milestones, and see their performance ranked on leaderboards, creating a clear and compelling feedback loop.
Platforms like Khan Academy masterfully use this system. Students earn "energy points" for watching videos and practicing skills, and achieve "mastery" badges for proficiency. This structure transforms learning from a passive activity into an active quest for accumulation and achievement. The PBL model is one of the most visible and widely adopted gamification examples in education because of its straightforward implementation and immediate motivational impact.
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: While PBL is primarily extrinsic, badges can tap into intrinsic needs for competence and accomplishment. Earning a badge for mastering a tough concept provides a tangible symbol of intellectual growth.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Points act as a direct reward, while leaderboards introduce a competitive element. This social pressure encourages students to keep up with their peers and strive for higher rankings.
- Progress Visualization: The entire PBL system serves as a transparent progress tracker. Students can instantly see how much they've accomplished (points), what milestones they've hit (badges), and how they measure up (leaderboards).
Key Insight: The effectiveness of PBL lies in its ability to make learning progress visible and quantifiable. It provides immediate, structured feedback that helps students understand where they are, what they have achieved, and what they need to do next.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Make Badges Meaningful: Tie badges to specific, meaningful learning outcomes, not just task completion. A "Critical Thinker" badge is more impactful than a "Homework Done" badge.
- Design Dynamic Leaderboards: Instead of a single leaderboard showing top scores, create leaderboards that highlight "most improved," "most persistent," or "best collaborator" to give more students a chance to shine.
- Use Points for More Than Grades: Connect points to low-stakes classroom privileges or rewards, separating them from formal assessment to reduce anxiety and encourage risk-taking.
- Balance Competition and Collaboration: Pair leaderboards with group projects where teams earn points together. This fosters teamwork while still leveraging the motivational pull of competition.
3. Minecraft Education Edition
Minecraft Education Edition takes one of the world's most popular video games and transforms it into a powerful educational tool for the classroom. This version is modified to give teachers control over the learning environment, allowing them to embed curricular content directly into immersive, block-based virtual worlds. Students engage with subjects like history, science, and math through hands-on exploration, collaborative building, and creative problem-solving.

The platform brilliantly leverages the core gameplay loop that made Minecraft a global phenomenon: exploration, resource gathering, and creation. By placing academic challenges within this engaging framework, it taps into students' natural curiosity and desire to build. This is a premier example of how gamification in education can transform abstract concepts into tangible, interactive experiences.
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: The freedom to create and explore fosters a sense of autonomy and purpose. Students are driven by their own curiosity to discover, build, and solve problems within the game world, making learning a self-directed activity.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Collaborative projects and classroom challenges introduce a social dynamic where students work toward shared goals. Completing a complex build or solving a puzzle as a team provides a powerful sense of collective achievement.
- Habit Formation: Unlike simple reward systems, Minecraft encourages sustained engagement through long-term projects. The desire to see a virtual city, historical monument, or ecosystem simulation completed motivates students to return to the task day after day.
Key Insight: Minecraft Education Edition's strength is its ability to create a "learning by doing" environment at scale. It makes abstract concepts tangible and gives students agency over their educational journey.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Start with Pre-Built Worlds: Begin with the extensive library of pre-made lessons and worlds to familiarize yourself and your students with the platform before creating custom content.
- Integrate Coding Gradually: Use the "Code Builder" feature to introduce basic programming concepts in a fun, visual context that directly impacts the game world.
- Set Clear Objectives: Establish clear learning goals and behavioral expectations before allowing free-building to ensure activities remain focused and productive.
- Connect to Curriculum: Pair in-game activities with offline reflection, discussions, or written assignments to solidify learning and assess student understanding. You can find a vast community and resources at the official Minecraft Education website.
4. Kahoot! Interactive Quiz Gamification
Kahoot! is a powerful game-based learning platform that has revitalized the classroom quiz, turning it into a high-energy, competitive social event. It allows educators to create or select pre-made quizzes, called "kahoots," which students answer in real-time on their own devices. Points are awarded for both speed and accuracy, with a live leaderboard fueling excitement and engagement.
The platform's genius lies in its ability to combine formative assessment with genuine fun. The immediate feedback and social competition transform knowledge review from a passive activity into an active, memorable experience. This approach is a leading example of how gamification examples in education can boost participation and knowledge retention in a group setting.
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: The fast-paced music, vibrant visuals, and immediate right/wrong feedback create an exciting and rewarding atmosphere that makes students eager to participate and test their knowledge.
- Extrinsic Motivation: The real-time leaderboard is the core driver of competition. Seeing their name climb the ranks provides a powerful incentive for students to focus and answer quickly and correctly.
- Habit Formation: While not focused on daily streaks, Kahoot! builds a positive association with learning and assessment. Consistently using it for reviews can make students look forward to testing their understanding rather than dreading it.
Key Insight: Kahoot!'s strength is its mastery of social and competitive dynamics. It leverages the classroom environment to create a shared, high-energy learning moment that motivates through peer competition and collective excitement.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Use as a Formative Tool: Employ Kahoot! for low-stakes review sessions or to gauge understanding before a major test, not for final grades.
- Facilitate Discussion: After each question, take a moment to discuss why the correct answer is right and address common misconceptions revealed by the results.
- Promote Collaboration: Switch to team mode, where students work together. This encourages peer-to-peer learning and reduces individual pressure.
- Explore Alternatives: While Kahoot! stands out, many tools offer similar interactive experiences. Explore some of the alternative interactive quiz platforms to find the best fit for your classroom's needs.
5. Role-Playing Games (RPGs) and Quest-Based Learning
Quest-based learning transforms the entire classroom into an immersive role-playing game. Students adopt character personas and embark on epic "quests" that are actually curriculum-aligned learning activities. Platforms like Classcraft and innovative schools like Quest to Learn have pioneered this model, where completing homework, collaborating with peers, and demonstrating knowledge allow students to level up their characters and unlock new abilities.
This approach recasts students as the heroes of their own learning journey. Instead of passively receiving information, they actively solve problems and overcome challenges within a compelling narrative. This method is one of the most comprehensive gamification examples in education because it restructures the learning environment itself, turning assignments into missions and grades into experience points (XP).
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: The narrative and character progression create a strong sense of purpose and autonomy. Students are motivated by the desire to advance the story and develop their character, making the learning process personally meaningful.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Tangible rewards like XP, virtual items, and new character powers serve as powerful external incentives. These rewards are directly tied to academic effort and positive classroom behavior.
- Collaborative Learning: Many RPG models, like Classcraft, group students into "guilds" or "teams." This encourages peer support, as a team's success in a "boss battle" (a major test or project) depends on every member's contribution.
Key Insight: RPGs and quest-based learning excel at contextualizing education. By embedding academic tasks within a larger narrative, they answer the age-old student question, "Why do I need to learn this?" The answer becomes clear: to defeat the dragon, save the kingdom, or complete the quest.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Start with a Single Quest: Before building an entire RPG world, design a single "quest" for an upcoming unit. Frame the learning objectives as the quest's main goal and individual assignments as steps to achieve it.
- Align Mechanics with Learning: Ensure game mechanics reinforce educational goals. For example, a "wisdom" statistic could increase when a student completes research tasks, or a "crafting" skill could be leveled up through project-based assignments.
- Create a Compelling Narrative: Develop a simple but engaging story for your classroom. The narrative provides context and makes the "game" feel cohesive and immersive.
- Use Character Progression as Motivation: Allow students to create and customize characters that gain new skills or cosmetic items as they master academic concepts. This visual representation of progress is a powerful motivator.
6. Adaptive Learning Systems with Personalized Pathways
Adaptive learning systems represent a sophisticated form of gamification that uses AI to create personalized educational journeys. Platforms like ALEKS and DreamBox Learning analyze a student's performance in real time, adjusting the difficulty and sequence of content to match their specific needs. This creates a tailored "learning pathway" where each student progresses at their own pace, tackling challenges that are neither too easy nor too difficult.
The power of these systems lies in their ability to maintain an optimal level of challenge, a core principle of game design known as the "flow state." By constantly adapting, they prevent the boredom that comes from easy material and the frustration that arises from overly difficult tasks. This makes them a compelling example of how gamification in education can be deeply personalized and highly effective.
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: The feeling of mastering a concept before moving on provides a powerful sense of competence and accomplishment. The system ensures students are always working within their "zone of proximal development," making learning feel challenging yet achievable.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Progress is often visualized through skill trees, completion percentages, or unlocked levels. Seeing their personal "knowledge map" fill up provides a clear, tangible reward for their effort.
- Habit Formation: These systems encourage continuous engagement by presenting an endless-seeming series of perfectly matched challenges. Students are motivated to log in to conquer the "next" topic in their personalized queue, fostering a consistent learning routine.
Key Insight: Adaptive learning systems gamify the learning process by treating it as a personal quest. The algorithm acts as a guide, ensuring the journey is always challenging but never impossible, which maximizes engagement and mastery.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Define Mastery: Clearly establish what it means to "master" a topic before letting students advance. Use the system's data to confirm understanding.
- Blend Tech with Touch: Use the analytics from adaptive platforms to identify which students need one-on-one help or small group instruction. The technology should inform, not replace, your teaching.
- Monitor Progress Actively: Watch for students who are "gaming the system" by rushing through content. Use the platform's data to guide conversations about thoughtful engagement.
- Leverage AI for Personalization: Embrace how AI-driven tools can provide individualized practice, freeing up your time for higher-level instruction and support. You can explore this further in our guide to the role of AI in adaptive learning.
7. Badges and Micro-Credentials Systems
Badges and micro-credentials represent a shift from broad, traditional grades to a more granular system of recognizing specific skills. These digital (or physical) symbols act as verifiable proof that a learner has mastered a particular competency, from coding a basic function to demonstrating leadership in a group project. This approach provides a clearer, more detailed picture of a student's abilities.
This system breaks down learning into discrete, achievable goals, each with a tangible reward. Unlike a final grade that averages out performance, badges allow students to showcase specific strengths and build a portfolio of verified skills. This method is a powerful example of how gamification in education can directly link learning activities to real-world value and recognition.
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: The act of earning a badge for a specific skill provides a powerful sense of accomplishment and mastery. It validates effort on a micro-level, encouraging students to tackle new challenges to "collect" more skills.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Badges serve as social signifiers of achievement. When shared on platforms like LinkedIn or in digital portfolios, they offer external validation and can even be aligned with industry standards or career pathways.
- Goal Clarity: Each badge is tied to a specific, transparent set of criteria. This clarity eliminates ambiguity about what is required for success, allowing students to focus their efforts on a well-defined target and understand exactly what they need to do to succeed.
Key Insight: The power of badges lies in their ability to make learning visible and portable. They transform abstract knowledge into concrete, shareable credentials that students can use to build a personalized record of their unique skills and accomplishments.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Define Clear Criteria: For each badge, create a detailed and transparent rubric that outlines the exact requirements for earning it. Students should know precisely what they need to demonstrate.
- Align with Broader Goals: Connect badges to larger learning objectives, curriculum standards, or even recognized industry credentials to give them real-world value and context.
- Create Visual Appeal: Design visually distinct and appealing badges for different skills or achievement levels. A strong visual identity makes the reward more desirable and memorable.
- Promote Portfolio Building: Encourage students to collect their badges in a digital portfolio where they can reflect on their learning journey and showcase their diverse skill set to others. Explore how digital credentials work on the Credential Engine platform.
8. Simulation-Based Learning and Virtual Labs
Simulation-based learning transforms education by placing students in dynamic, interactive digital environments. Platforms like Labster and PhET Interactive Simulations allow learners to conduct complex experiments, manipulate variables, and explore scientific principles in a safe, controlled, and repeatable setting. This approach gamifies the scientific process, turning inquiry and discovery into an engaging game of "what if?"

These virtual labs remove the constraints of physical resources, cost, and safety, enabling students to perform experiments that would be impossible in a traditional classroom. The success of this gamification example in education lies in its ability to make abstract concepts tangible and to empower students to learn through consequence-free experimentation.
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: The freedom to explore, experiment, and see immediate outcomes fuels natural curiosity and a desire for discovery. Students are driven by the challenge of solving a problem or understanding a phenomenon.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Many platforms include guided missions, points for correctly completing procedures, and badges for mastering specific lab techniques, providing clear goals and a sense of achievement.
- Mastery Learning: Simulations allow for infinite retries. If an experiment fails, students can simply reset and try a new approach, reinforcing the idea that learning comes from iteration and understanding mistakes, not just from getting it right the first time.
Key Insight: Virtual labs gamify the core scientific method of hypothesis, experimentation, and conclusion. They make failure a safe and valuable part of the learning loop rather than a point of discouragement.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Complement, Don't Replace: Use virtual labs to prepare for or supplement physical experiments. Let students practice a procedure virtually before attempting it with real equipment.
- Guide the Inquiry: Start with structured simulations that have clear objectives and procedures before moving on to more open-ended, exploratory labs.
- Focus on Data Interpretation: After a virtual experiment, task students with analyzing the data they collected, drawing conclusions, and connecting their findings to real-world theories.
- Debrief and Discuss: Facilitate a classroom discussion where students can share their results, discuss unexpected outcomes, and explain the scientific principles they observed in action.
9. Progress Bars, Skill Trees, and Leveling Systems
Progress bars, skill trees, and leveling systems are foundational gamification mechanics that provide learners with a clear, visual representation of their advancement. These tools transform an abstract learning journey into a tangible path, where each completed task contributes to a visible milestone. Platforms like Khan Academy and Codecademy use them to show students exactly how far they've come and what they need to learn next.
This approach effectively maps out the curriculum, giving students a sense of agency and control over their learning path. By visualizing progress, these systems make the accumulation of knowledge feel more concrete and rewarding, motivating learners to push forward to the next level or unlock the next skill. This is one of the most powerful gamification examples in education for structuring complex subjects.
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: Skill trees offer learners choice and autonomy in their educational path, allowing them to specialize in topics that genuinely interest them.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Leveling up and completing progress bars provide clear, quantifiable achievements that serve as external rewards and status indicators.
- Goal Setting: These systems break down a large curriculum into a clear sequence of smaller, achievable goals, reducing overwhelm and making the ultimate objective seem more attainable.
Key Insight: The power of visual progression lies in its ability to make learning feel like a journey of constant, measurable growth. It provides a clear answer to the student's question, "What's next?" and reinforces the value of their effort.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Map Your Curriculum: Design a "skill tree" where foundational concepts unlock more advanced topics, visually guiding students through the course material.
- Use Progress Trackers: Implement simple progress bars for long-term projects or modules to help students visualize their progress toward completion.
- Celebrate Milestones: Create "level-up" moments when students master a key concept or complete a unit, offering recognition or small rewards.
- Offer Branching Paths: Where possible, allow students to choose which topics to tackle next, fostering autonomy. For a deeper look into motivational systems that avoid frustrating learners, explore our insights on alternatives to restrictive learning models.
10. Collaborative and Cooperative Gaming Mechanics
Shifting the focus from individual competition to collective achievement, collaborative gaming mechanics use gamification to foster teamwork and shared success. This approach turns learning into a team sport where students must combine their strengths, communicate effectively, and work together to overcome challenges, mirroring real-world professional environments. Examples range from Classcraft's team-based quests to multiplayer challenges in Minecraft: Education Edition.
The power of this method lies in its ability to build soft skills like communication, problem-solving, and empathy alongside academic knowledge. By designing tasks that require diverse inputs, educators can ensure every student has a crucial role to play. This cooperative framework is a standout example of how gamification in education can create a supportive and interdependent classroom culture.
Strategic Breakdown
- Intrinsic Motivation: Students gain a sense of belonging and purpose by contributing to a group effort. The shared struggle and collective victory create a powerful emotional investment in the learning process.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Team-based rewards, such as group points, shared badges, or unlocking a class-wide privilege, encourage positive interdependence. The success of one member benefits the entire group.
- Skill Development: These mechanics inherently require students to practice negotiation, active listening, and conflict resolution. The game-like context provides a safe space to develop these essential interpersonal skills.
Key Insight: Collaborative gamification transforms learning from an isolated activity into a shared social experience. It leverages peer-to-peer motivation and accountability to drive engagement and deepen understanding for all members of the group.
Actionable Takeaways for Educators
- Assign Clear Roles: Define specific responsibilities within each team (e.g., "Scribe," "Timekeeper," "Spokesperson") to ensure equitable participation and individual accountability.
- Design Interdependent Tasks: Create challenges where no single student has all the information or skills needed for success, forcing them to rely on each other.
- Celebrate Team Contributions: Publicly recognize group achievements and highlight specific examples of excellent teamwork to reinforce cooperative behaviors.
- Use Round-Robin Feedback: Implement structured peer feedback sessions where team members can share constructive thoughts on the group's process and dynamics, fostering metacognitive skills. You can learn more about implementing these systems from platforms like Classcraft, which excels at cooperative gameplay.
Gamification in Education: 10 Examples Compared
| Solution | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resources & Efficiency ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases & Tips 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duolingo Language Learning App | 🔄 Low — ready-made mobile/web product, minimal setup | ⚡ Low resources; affordable (free–premium); efficient for daily microlearning | 📊 Strong vocabulary retention and engagement; limited grammar/conversational depth | 💡 Self-paced daily practice, classroom supplement; pair with real conversations | ⭐ Very high engagement and scalability via gamification |
| Points, Badges, and Leaderboards (PBL) Systems | 🔄 Low — straightforward mechanics to add to platforms | ⚡ Low–Medium; easy to implement, highly customizable | 📊 Raises motivation and measurable participation; may not drive deep learning | 💡 Use private/rotating leaderboards and meaningful badges | ⭐ Simple, transparent motivation and progress tracking |
| Minecraft Education Edition | 🔄 Medium–High — requires curriculum design and teacher training | ⚡ Medium resources; needs devices, network; cost-effective for schools | 📊 High engagement, creativity, collaboration; strong cross-curricular application | 💡 Start with pre-built worlds; set behavior expectations and debrief | ⭐ Immersive environments that foster problem-solving and creativity |
| Kahoot! Interactive Quiz Gamification | 🔄 Low — fast setup for live sessions | ⚡ Low resources; works on students' devices; very time-efficient | 📊 Excellent for recall and formative checks; favors speed over depth | 💡 Use for review and low-stakes assessment; mix with other methods | ⭐ Immediate feedback and high classroom engagement |
| RPGs & Quest-Based Learning | 🔄 High — complex narrative and mechanic design | ⚡ Medium–High; time-intensive to build and run | 📊 Deep engagement and improved retention; supports persistence and empathy | 💡 Start small with single quests; align mechanics to objectives | ⭐ Highly immersive, promotes intrinsic motivation and sustained effort |
| Adaptive Learning Systems | 🔄 High — integration, data pipelines, and algorithm tuning | ⚡ High resources; needs data infrastructure and training | 📊 Personalized progress; often 30–40% faster learning for targeted skills | 💡 Use alongside teachers; train staff to act on analytics | ⭐ Highly personalized instruction and predictive support |
| Badges & Micro-Credentials Systems | 🔄 Medium — requires rubric design and issuing workflows | ⚡ Medium resources; platforms for issuing and verifying badges | 📊 Granular demonstration of skills; portable credentials for careers | 💡 Create clear rubrics; align to standards and promote portfolios | ⭐ Recognizes specific competencies and supports competency-based pathways |
| Simulation-Based Learning & Virtual Labs | 🔄 Medium–High — design realistic scenarios and assessments | ⚡ Medium resources; software and capable devices required | 📊 Improves conceptual understanding (~20–30%); safe repeatable practice | 💡 Pair with physical labs and structured debriefs; set clear objectives | ⭐ Safe, cost-effective experimentation and strong visual learning |
| Progress Bars, Skill Trees & Leveling Systems | 🔄 Low–Medium — UI design and prerequisite mapping | ⚡ Low resources; easy to add to existing platforms | 📊 Increases completion rates (~25–35%); clarifies learning path | 💡 Design trees to reflect real prerequisites; celebrate milestones | ⭐ Clear visualization of progress that sustains motivation |
| Collaborative & Cooperative Gaming Mechanics | 🔄 Medium — requires social design and facilitation | ⚡ Medium resources; may need coordination tools and scaffolds | 📊 Improves collaboration, classroom climate, and peer learning | 💡 Teach collaboration skills, assign roles, include individual accountability | ⭐ Builds teamwork, communication, and social-emotional skills |
The Future of Learning is Playful: Key Takeaways for Educators
Throughout this extensive exploration of gamification examples in education, a powerful, unifying theme has emerged. The future of learning isn't about replacing teachers with games; it's about empowering educators and learners with the psychological drivers that make games so compelling. The shift from passive information consumption to active, engaged participation is the core revolution.
We've moved beyond the superficial application of points and badges. The most effective strategies, as seen in Minecraft Education's collaborative worlds or the personalized pathways of adaptive learning systems, embed game mechanics deep within the pedagogical structure. They don't just reward completion; they celebrate effort, encourage experimentation, and make the process of learning itself intrinsically rewarding.
Synthesizing the Core Principles of Effective Gamification
Distilling the diverse examples from Duolingo's streaks to Kahoot!'s competitive quizzes, several foundational principles become clear. True educational gamification is not a one-size-fits-all solution but a strategic framework built on understanding human motivation.
Here are the most critical takeaways for any educator, instructional designer, or platform developer looking to implement these ideas:
- Purpose Over Points: The "why" behind a game mechanic is more important than the mechanic itself. A leaderboard is meaningless without a sense of community and friendly competition. A badge is just a digital sticker unless it represents the mastery of a genuinely challenging and valuable skill. Always ask: Does this element directly support a specific learning outcome?
- Balancing Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation: While extrinsic rewards like points and levels can provide initial momentum, sustainable engagement comes from fostering intrinsic motivation. This is achieved through mechanics that grant learners autonomy (choice in their learning path), mastery (clear feedback and progress), and purpose (connecting lessons to real-world applications or a larger narrative).
- The Power of Immediate Feedback: A key reason games are so addictive is their constant feedback loop. You know instantly if you’ve succeeded or failed, allowing for rapid iteration and learning. Tools like Kahoot! and adaptive systems excel at this, providing instant gratification and correction that traditional grading cycles cannot match.
Strategic Insight: The most successful gamification examples in education are those that seamlessly merge the learning objective with the game's core loop. The "fun" part is not a distraction from the learning; it is the process of learning.
Your Actionable Roadmap to a Gamified Classroom
Feeling inspired is one thing; implementing these strategies is another. The journey from theory to practice doesn't have to be overwhelming. You can begin integrating these powerful concepts into your educational environment today.
Start by identifying a single, specific challenge in your curriculum. Is it student disengagement during review sessions? Difficulty in grasping abstract concepts? A lack of collaborative spirit? Once you've defined the problem, use the examples we've covered as a toolbox.
- For Engagement: Consider a low-stakes, high-energy quiz using a tool like Kahoot! to transform a mundane review into an exciting competition.
- For Complex Concepts: Use a quest-based model. Frame a multi-step project as an epic journey with milestones (levels), specific deliverables (quests), and a final "boss battle" (the final presentation or exam).
- For Collaboration: Leverage mechanics from cooperative games. Design group projects where each student has a unique role or skill, requiring them to work together to "win" by completing the assignment. This mirrors the collaborative problem-solving seen in Minecraft.
Mastering these approaches is no longer a niche skill; it is becoming a fundamental component of modern pedagogy. By thoughtfully applying these gamification examples in education, you can create a more resilient, motivated, and successful learning environment that prepares students not just for tests, but for a lifetime of curious exploration. The goal is to cultivate an atmosphere where students are not just pushed to learn, but are pulled forward by their own ambition and curiosity.
Ready to see how these principles create a truly engaging and effective learning experience? Polychat leverages core gamification mechanics like timed challenges, progress tracking, and interactive AI conversation games to help you master a new language without limits. Experience the future of playful learning and start your journey to fluency today at Polychat.
Related Posts
Best free language learning apps: Top picks for 2025 to boost fluency
Explore the best free language learning apps for 2025 with quick reviews, features, and tips to start speaking confidently.
Read moreHow Interactive Games are Transforming Cultural & Travel Content
Discover how embedding interactive language games can double your website's engagement, lower bounce rates, and turn passive readers into active participants.
Read moreHow to Say Goodbye in Spanish Like a Native Speaker
Learn how to say goodbye in Spanish beyond just 'adiós'. Master casual, formal, and regional farewells to sound natural in any conversation.
Read more